Have you ever heard about “Biodegradable plastics”? What do you know about them? What are the components and applications used to make these kinds of plastics? Why are they called “biodegradable”? Are there any environmental consequences of these kinds of plastics? Let’s further explore and find the answers for these questions.
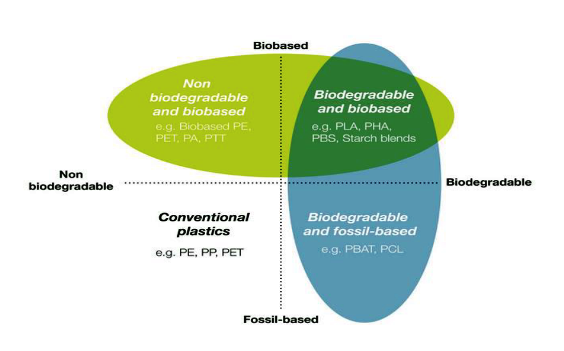
Biodegradable plastics are products that are commonly produced by using one or more of the three following materials: renewable raw materials, micro-organisms, and petrochemicals. They are designed to be used mainly in the packaging industry and then at the end of its life cycle to biodegrade and compost by the actions of many living organisms such as microbes in water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. In general, they meet the specifications of the American Society for Testing and Materials document - ASTM D 6400-99 - entitled "Standard Specifications for Compostable Plastics."
Biodegradable plastics are mainly made from renewable and all-natural plant materials, which may include starch, orange peels, corn oil, corn sugar and plants. Bioplastics include biodegradable plastics produced from fossil materials and bio-based plastics like plastics synthesized from biomass or renewable resources. Materials that make up bioplastics are not all biodegradable.
There are many raw materials that make up Bio-based plastics, including the following:
- Polylactic acid is a kind of thermoplastic synthesized from renewable biomass, specifically from fermented plant starch like sugar beet pulp, corn, cassava and sugarcane.
- Starch blends, which are a kind of thermoplastic polymer, are produced by using starch with plasticizers.
- Cellulose bioplastics, which are the cellulose esters and their derivatives.
- Lignin-based polymer composites, which are bio-renewable natural aromatic polymers with biodegradable properties.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates are biodegradable plastics that are naturally produced by many micro-organisms.
Biodegradable plastics can be used in various ways. One way is these kinds of plastics can be made into foam packaging materials by extruding, injection-molding and co-injecting with other plastic materials like LDPE and HDPE. In addition to that, there are many types of fillers with different colors and many granulation sizes that can be used in order to make different external appearances.
Some applications of biodegradable plastics in our daily life include the following:
- Single-use or short-term use is the most commonly used biodegradable plastics in the packaging industry, such as disposal tableware.
- The organic waste collection and diversion.
- In agriculture, for things such as mulch-films, seed blankets and plant pots.
- Food packaging for storage and transport.
- Medical practices
Biodegradability of plastic is when plastic can be decomposed of by the help of living microorganisms and when plastic can be converted into carbon dioxide and biomass and water. Degradation consists of three steps, such as the colonization of the plastic surface, hydrolysis, and mineralization. There are many factors affecting the ability of plastic to be degraded and these factors can be categorized in the following ways:
Chemical and Physical properties of the plastic, which include chemical structure, molecular weight, molecular weight distribution, surface area, hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties, melting temperature, crystallinity structure, polymer characteristics and nature of pre-treatment, the type of functional groups and other substituents present in its structure and additives or plasticizers added to the polymer.
- Abiotic factors which include temperature, atmospheric factors like water/salt concentration, hydrolysis.
- Biotic factors which include air, sunlight, presence of proper strains of microorganisms and type of organism.
Petroleum-based plastics are harmful to the environment unlike biodegradable plastics. There are many advantages of using biodegradable plastics as an alternative for the traditional plastics:
- Variety of durable plastics products for food storage and transport.
- The biodegradable plastics do not have chemicals that can are considered environmentally harmful chemicals and can be made from natural materials.
- The natural materials that are used in producing the biodegradable plastics can be safely returned to the environment at the end life of the product.
Disadvantages of biodegradable plastics
- The higher cost of energy and money used for producing biodegradable plastics than petroleum-based plastics.
- These kinds of plastics need air, sunlight, moisture, and a certain temperature and humidity, which means they need a composting environment to degrade.
- The best place for the biodegradable plastics to break down is in an oxygen-free environment, like a landfill.
- Biodegradable plastics could contain a certain kind of metal, which may be released into the environment and cause issues during the degradation process.
- The best strategy to focus on in order to solve the waste issue is reduction and recycling, not by producing more biodegradable.
- The biodegradable plastics may need 3-6 months in order to fully decompose in the best ideal conditions.
Some environmental and ecological concerns are:
- Biodegradation in the ocean: The remaining plastics that are not fully degraded will stay in the ocean and cause harm to the marine life.
- Oxo-biodegradation: Biodegradable plastic bags could release metals and may need a longer time period to degrade. Oxo-biodegradable plastics could make very tiny fragments of plastic, which will disrupt the degradation process.
- Effect on food supply: Very bad impact to human supply because of total carbon, fossil fuel and water usage in the production of biodegradable bioplastics using the natural resources.
- Methane: The danger of releasing methane during the degradation process in an anaerobic landfill environment.
Biodegradable plastics have many components, and advantages and disadvantages that are continuously being researched and applied to improve the packaging industry today.
References:
https://www.lawinsider.com/dictionary/biodegradable-plastic
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biodegradable_plastic
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2769161/ www.pepctplastics.com/resources/connecticut-plastics-learning-center/biodegradable-plastics/
www.bpiworld.org/resources/Documents/ASTM_D6400-99_Background.pdf www.globalresearchonline.net/journalcontents/v31-2/36.pdf
https://www.plasticseurope.org/en/about-plastics/what-are-plastics/large-family/biodegradable-plastics

